CasNo:532-32-1
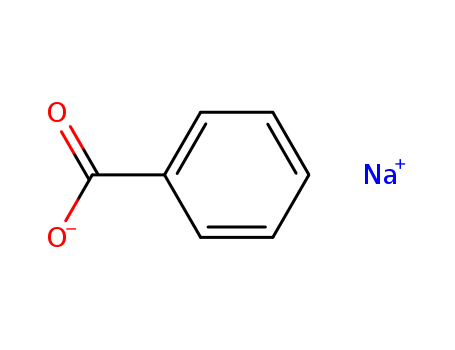
Product Name:Sodium benzoate
Molecular Formula:C7H5NaO2
Appearance:white crystalline powder
Purity:99%
Quality Factory Supply Sodium benzoate, Factory Sells 532-32-1 Customized Supply
- Molecular Formula:C7H5NaO2
- Molecular Weight:144.105
- Appearance/Colour:white crystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:0.0122mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:>300 °C(lit.)
- Boiling Point:249.3 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:4.03[at 20 ℃]
- Flash Point:111.4 °C
- PSA:40.13000
- Density:1,44 g/cm3
- LogP:0.05010
Sodium benzoate(Cas 532-32-1) Usage
|
description |
Sodium benzoate, also known as benzoic acid sodium, is commonly used as food preservatives in food industry, odorless or with slight smell of benzoin, and tastes sweet astringency. Stable in air, can absorb moisture in open air. It’s naturally found in blueberry, apple, plum, cranberry, prunes, cinnamon and cloves, with weaker antiseptic performance than benzoic acid. Antiseptic performance of 1.180g sodium benzoate is equivalent of about 1g benzoic acid. In acidic environment, sodium benzoate have obvious inhibitory effect on a variety of microorganisms: when pH is at 3.5, 0.05% solution can completely inhibit the growth of yeast; while when pH is above 5.5, it has poor effect on a lot of mold and yeast; hardly has any effect in alkaline solution. After sodium benzoate enters into the body, in the process of biotransformation, it would combine with glycine to be uric acid, or combine with glucuronic acid to be glucosiduronic acid, and all to be eliminated from the body in urine, not to accumulate in the body. As long as it is within the scope of the normal dosage, it would be harmless to the human body, and it is a safe preservatives. It also can be used for carbonated beverages, concentrated juice, margarine, chewing gum base, jam, jelly, soy sauce, etc. Human acceptable daily intake (ADI) < 5 mg/kg body weight (take benzoic acid as calculation basis). Sodium benzoate has big lipophilicity, and it is easy to penetrate cell membrane into the cells, interfere in permeability of cell membrane, and inhibit cell membrane’s absorption of amino acids; cause Ionization acidification of alkaline storage in the cell when entering into, inhibit activity of respiratory enzymes, and stop condensation reaction of acetyl coenzyme A, and thereby achieve the purpose of food antiseptic. The above information is edited by the Chemicalbook He Liaopu. |
|
Chemical properties |
White crystals or granules, or colorless powder, with sweet astringency. Soluble in water, ethanol, glycerol and methanol. |
|
Uses |
1. Sodium benzoate is also an important preservative of acid type food. It transforms into effective form of benzoic acid during application. See benzoic acid for application range and dosage. In addition, it also can be used as fodder preservative. 2. Preservatives; antimicrobial agent. 3. Sodium benzoate agent is a very important preservative of acid type fodder. It transforms into effective form of benzoic acid during application. See benzoic acid for application range and dosage. In addition, it also can be used as food preservative. 4. Used in the research of pharmaceutical industry and plant genetic, also used as dye intermediates, fungicide and preservatives. 5. The product is used as food additive (preservative), fungicide in pharmaceutical industry, dye mordant, plasticizer in plastic industrial, and also used as organic synthetic intermediate of spices and others. |
|
Content Analysis |
Take dried sample 1.5g into a 250ml conical flask, dissolve it with 25ml water, and then add 50ml ether and bromophenol. |
|
Toxicity |
ADI 0~5mg/kg (take benzoic acid as calculation basis, total value of ADI including benzoic acid and its salts and esters; FAO/WHO, 2001). LD50 4070mg/kg (rats, by oral). GRAS(FDA,§184.1733,2000). |
|
Production methods |
1. Neutralized by benzoic acid and sodium bicarbonate. Put water and sodium bicarbonate into the neutralizing pot, boil it and make it dissolved into sodium bicarbonate solution. Mix it with benzoic acid until PH value of the reaction solution reaches to 7-7.5. Heat it to emit over carbon dioxide, and then add active carbon to decolorize it for half an hour. Do suction filtration, after filtrate gets concentrated, put it into flaker tray, dry it to be sheets in the drum, crush it, and then sodium benzoate is made. Consumption rate of benzoic acid (99.5%) 1045kg/t and sodium bicarbonate (98%) 610kg/t. 2. Use 32% soda solution to neutralize benzoic acid in the pot to reach PH value of 7.5, and neutralization temperature is 70℃. Use 0.3% active carbon to decolorize the neutralized solution, vacuum filter it, concentrate, dry it and then it comes to powdered sodium benzoate. C6H5COOH+Na2CO3→C6H5COONa 3. To get it by toluene oxidation made benzoic acid reacting with sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide. |
|
Description |
Sodium benzoate has the chemical formula NaC7H5O2; it is a widely used food preservative, with E number E211. It is the sodium salt of benzoic acid and exists in this form when dissolved in water. It can be produced by reacting sodium hydroxide with benzoic acid. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Benzoic acid is almost odorless or exhibits a sweet, faint, balsamic odor and a sweet–sour to acrid taste. For a detailed description, refer to Burdock (1997). |
|
Occurrence |
Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and in animals. The salt is not found to occur naturally. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: An organic sodium salt resulting from the replacement of the proton from the carboxy group of benzoic acid by a sodium ion. |
|
Production Methods |
Sodium benzoate is prepared by adding benzoic acid to a hot concentrated solution of sodium carbonate until effervescence ceases. The solution is then evaporated, cooled and allowed to crystallize or evaporate to dryness, and then granulated. |
|
Preparation |
Produced by the neutralization of benzoic acid with sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide. |
|
General Description |
Sodium benzoate is a sodium salt of benzoic acid, that is freely soluble in water compared to benzoic acid. It is generally used as an antimicrobial preservative in cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals.Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards. |
|
Hazard |
Use in foods limited to 0.1%. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Sodium benzoate is used primarily as an antimicrobial preservative in cosmetics, foods, and pharmaceuticals. It is used in concentrations of 0.02–0.5% in oral medicines, 0.5% in parenteral products, and 0.1–0.5% in cosmetics. The usefulness of sodium benzoate as a preservative is limited by its effectiveness over a narrow pH range. Sodium benzoate is used in preference to benzoic acid in some circumstances, owing to its greater solubility. However, in some applications it may impart an unpleasant flavor to a product. Sodium benzoate has also been used as a tablet lubricant at 2–5% w/w concentrations. Solutions of sodium benzoate have also been administered, orally or intravenously, in order to determine liver function. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Sodium benzoate also has pharmaceutical applications and is component of syrup and transparent tablet. High levels of sodium benzoate may trigger histamine release and also induce cell damage. It is recommended for the treatment of urea cycle disorders. However, high levels of sodium benzoate may contribute to glycine deficiency and may impose neuromodulatory effects. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by subcutaneous and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion, intramuscular, and intraperitoneal routes. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Larger doses of 8-10 g by mouth may cause nausea and vomiting. Small doses have little or no effect. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Na2O. See also BENZOIC ACID. |
|
Safety |
Ingested sodium benzoate is conjugated with glycine in the liver to yield hippuric acid, which is excreted in the urine. Symptoms of systemic benzoate toxicity resemble those of salicylates. Whereas oral administration of the free-acid form may cause severe gastric irritation, benzoate salts are well tolerated in large quantities: e.g. 6 g of sodium benzoate in 200mL of water is administered orally as a liver function test. Clinical data have indicated that sodium benzoate can produce nonimmunological contact urtcaria and nonimmunological immediate contact reactions. However, it is also recognized that these reactions are strictly cutaneous, and sodium benzoate can therefore be used safely at concentrations up to 5%. However, this nonimmunological phenomenon should be considered when designing formulations for infants and children. Other adverse effects include anaphylaxis and urticarial reactions, although a controlled study has shown that the incidence of urticaria in patients given benzoic acid is no greater than that with a lactose placebo. It has been recommended that caffeine and sodium benzoate injection should not be used in neonates; however, sodium benzoate has been used by others in the treatment of some neonatal metabolic disorders. It has been suggested that there is a general adverse effect of benzoate preservatives on the behavior of 3-yearold children, which is detectable by parents, but not by a simple clinical assessment. The WHO acceptable daily intake of total benzoates, calculated as benzoic acid, has been estimated at up to 5 mg/kg of bodyweight. LD50 (mouse, IM): 2.3 g/kg LD50 (mouse, IV): 1.4 g/kg LD50 (mouse, oral): 1.6 g/kg LD50 (rabbit, oral): 2.0 g/kg LD50 (rat, IV): 1.7 mg/kg LD50 (rat, oral): 4.1 g/kg |
|
Potential Exposure |
Sodium benzoate is used as a food and feed additive, flavor, packaging material; pharmaceutical; preservative for food products and tobacco; anti-fungal agent; antiseptic, rust, and mildew inhibitor; intermediate in the manufacture of dyes. Used as a human hygiene biocidal product. |
|
storage |
Aqueous solutions may be sterilized by autoclaving or filtration. The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container, in a cool, dry place. |
|
Shipping |
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise it from EtOH (12mL/g). [Beilstein 9 IV 27.] |
|
Properties and Applications |
TEST ITEMS SPECIFICATION APPEARANCE WHITE POWDER CONTENT OF SODIUM BENZOATE 99.0% min DRY LOSS 0.10% max pH VALUE 8 TOTAL CHLORIDE 300 ppm max TRANSPARENCE PASS TOTAL HEAVY METAL 0.001% max As CONTENT 0.0002% max |
|
TEST ITEMS |
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE |
WHITE POWDER |
|
CONTENT OF SODIUM BENZOATE |
99.0% min |
|
DRY LOSS |
0.10% max |
|
pH VALUE |
8 |
|
TOTAL CHLORIDE |
300 ppm max |
|
TRANSPARENCE |
PASS |
|
TOTAL HEAVY METAL |
0.001% max |
|
As CONTENT |
0.0002% max |
|
Mechanism of food preservation |
The mechanism starts with the absorption of benzoic acid into the cell. If the intracellular pH changes to 5 or lower, the anaerobic fermentation of glucose through phosphofructokinase is decreased by 95 %, thereby inhibiting the growth and survival of micro-organisms that cause food spoilage. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Incompatible with quaternary compounds, gelatin, ferric salts, calcium salts, and salts of heavy metals, including silver, lead, and mercury. Preservative activity may be reduced by interactions with kaolin or nonionic surfactants. |
|
Regulatory Status |
GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (dental preparations; IM and IV injections; oral capsules, solutions and tablets; rectal; and topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. |
|
Who Evaluation |
Evaluation year: 1996 |
InChI:InChI=1/C7H6O2.Na/c8-7(9)6-4-2-1-3-5-6;/h1-5H,(H,8,9);/q;+1/p-1
532-32-1 Relevant articles
Sodium benzoate in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy: A double-blind randomized trial
S. Sushma, S. Dasarathy, Dr. Rakesh K. Tandon, Satish Jain, Surya Gupta, Mahender S. Bhist
, Hepatology, Volume16, Issue1 July 1992 Pages 138-144
Seventy-four consecutive patients with cirrhosis or surgical portasystemic anastamosis and hepatic encephalopathy of less than 7 days duration were randomized to receive lactulose (dose adjusted for 2 or 3 semiformed stools/day) or sodium benzoate (5 gm twice daily).
Treatment with sodium benzoate leads to malformation of zebrafish larvae
Huey-Jen Tsay a, Yun-Hsin Wang b, Wei-Li Chen b, Mei-Yun Huang b, Yau-Hung Chen b
, Neurotoxicology and Teratology Volume 29, Issue 5, September–October 2007, Pages 562-569
Sodium benzoate (C7H5NaO2) was dissolved in sterile distilled water to the desired concentrations. For dose titration, wt embryos at 48 h post-fertilization (hpf)
532-32-1 Process route
-
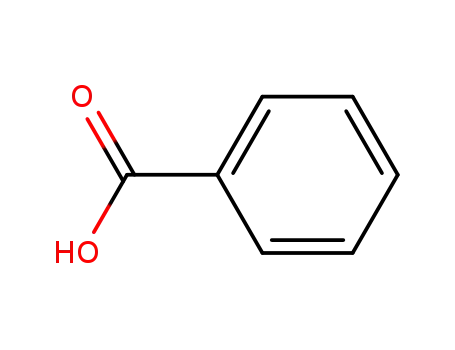
- 65-85-0,8013-63-6
benzoic acid

-
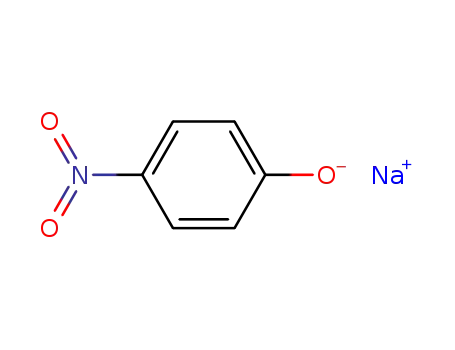
- 824-78-2
4-nitrophenol sodium salt

-
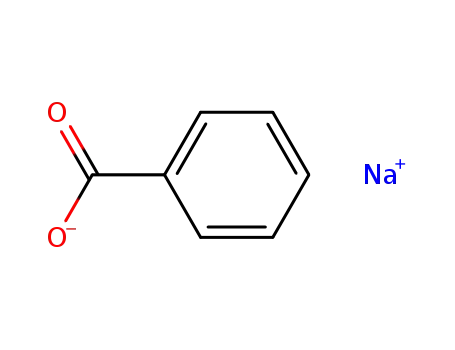
- 532-32-1
sodium benzoate

-
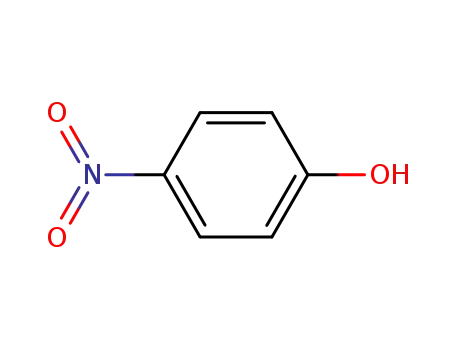
- 100-02-7,78813-13-5,89830-32-0
4-nitro-phenol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With 1-butyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium bis-(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide; In methanol; at 24.84 ℃; Reagent/catalyst; Equilibrium constant;
|
-
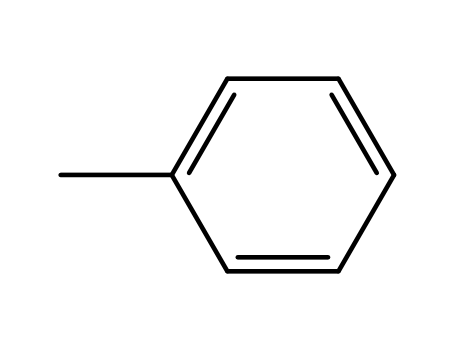
- 108-88-3,15644-74-3,16713-13-6
toluene

-

- 532-32-1
sodium benzoate

-
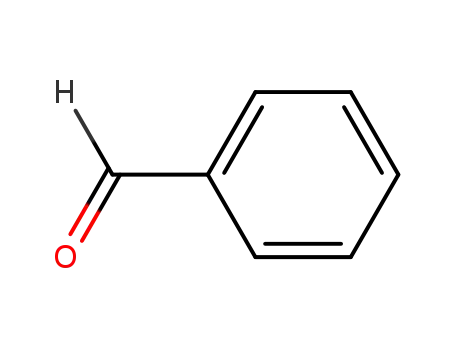
- 100-52-7
benzaldehyde

-
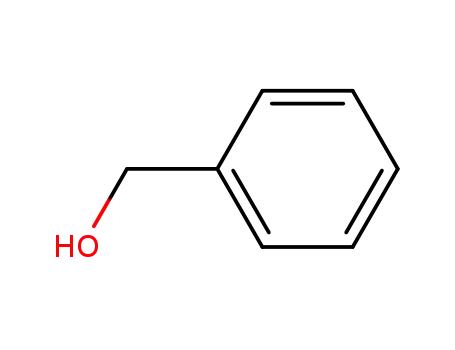
- 100-51-6,185532-71-2
benzyl alcohol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With potassium peroxodiphosphate; water; In phosphate buffer; pH=4.0 - 7.1; Product distribution; flash-photolysis;
|
41% 4% |